GPS comparison tests: verschil tussen versies
| Regel 1: | Regel 1: | ||
For an introduction, see also [[GPS]]. | For an introduction, see also [[GPS]]. | ||
Below are screenshots taken on September 29, 2024, during a walk in the park. In one hand, I held an iPhone 14 (with dual-band GPS), and in the other, an iPhone 12 (without dual-band GPS). I used this [https://openbomenkaart.org/obk8.htm?data=leiden&log test version]. (on a [http://localhost:8000/obk_test.htm?test&log desktop browser] it simulates gps random walk) | Below are screenshots taken on September 29, 2024, during a walk in the park, under a clear sky. In one hand, I held an iPhone 14 (with dual-band GPS), and in the other, an iPhone 12 (without dual-band GPS). I used this [https://openbomenkaart.org/obk8.htm?data=leiden&log test version]. (on a [http://localhost:8000/obk_test.htm?test&log desktop browser] it simulates gps random walk) | ||
For testing purposes, the OpenBomenKaart application uses diagnostic tweaks, as shown in the screenshots. | For testing purposes, the OpenBomenKaart application uses diagnostic tweaks, as shown in the screenshots. | ||
| Regel 16: | Regel 16: | ||
In the live app, the circles work best at zoom level 19 or higher. The red line works best at zoom level 18 or lower. | In the live app, the circles work best at zoom level 19 or higher. The red line works best at zoom level 18 or lower. | ||
<table><tr> | |||
<td>[[bestand:IMG 2081.PNG|200px|left|thumb|iPhone 12, note how by far the most measurements were at accuracy 2]]</td> | |||
<td>[[bestand:IMG 1966.PNG|200px|left|thumb|iPhone 14, note how by far the most measurements were at accuracy 3]]</td> | |||
</tr></table> | |||
<table><tr> | |||
<td>[[bestand:IMG 1964.PNG|200px|left|thumb|Closer view, zoomed in:<br>I started and ended here, then walked in a straight line, hard to tell]]</td> | |||
<td>[[bestand:IMG 1965.PNG|200px|left|thumb|test]]</td> | |||
</tr></table> | |||
<table><tr> | |||
<td>[[bestand:IMG 2083.PNG|200px|left|thumb|iPhone 12]]</td> | |||
<td>[[bestand:IMG 1967.PNG|200px|left|thumb|iPhone 14, note how this trace goes awry at Constantijn Huygenslaan 7-19, both iphones were at the same position, I never made this detour]]</td> | |||
</tr></table> | |||
<table><tr> | |||
<td>[[bestand:IMG 2084.PNG|200px|left|thumb|iPhone 12 only the numbers]]</td> | |||
<td>[[bestand:IMG 2085.PNG|200px|left|thumb|iPhone 14 only the numbers]]</td> | |||
</tr><tr> | |||
<td>[[bestand:IMG 1968.PNG|200px|left|thumb|test]]</td> | |||
<td>[[bestand:IMG 1969.PNG|200px|left|thumb|test]]</td> | |||
</tr></table> | |||
Evaluation: Both iPhones are able to render the route followed with reasonable accuracy when zoomed out. However, upon closer inspection (when zoomed in), the discrepancy can be confusing. The exact position can be off by 10 meters or more from what is reported. During normal use, this can be mitigated by waiting for the blue dot to stabilize, similar to Google Maps. However, in an unstructured area, like a park, it may not be as easy to detect discrepancies using visual cues. We actually need higher precision than Google Maps (since in Google Maps, if the blue dot is a few meters outside a bicycle lane, no one will be confused). | Evaluation: Both iPhones are able to render the route followed with reasonable accuracy when zoomed out. However, upon closer inspection (when zoomed in), the discrepancy can be confusing. The exact position can be off by 10 meters or more from what is reported. During normal use, this can be mitigated by waiting for the blue dot to stabilize, similar to Google Maps. However, in an unstructured area, like a park, it may not be as easy to detect discrepancies using visual cues. We actually need higher precision than Google Maps (since in Google Maps, if the blue dot is a few meters outside a bicycle lane, no one will be confused). | ||
Versie van 29 sep 2024 16:19
For an introduction, see also GPS.
Below are screenshots taken on September 29, 2024, during a walk in the park, under a clear sky. In one hand, I held an iPhone 14 (with dual-band GPS), and in the other, an iPhone 12 (without dual-band GPS). I used this test version. (on a desktop browser it simulates gps random walk)
For testing purposes, the OpenBomenKaart application uses diagnostic tweaks, as shown in the screenshots.
The exact path I walked is marked in cyan. I traced this route on the desktop using Esri imagery via tool keene.edu/campus/maps/tool/. I consider this my reference track. Note that Esri and OSM may not always align perfectly, especially for paths in the park.
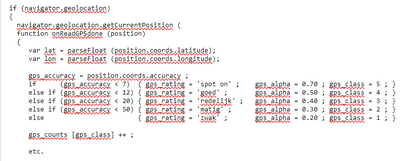
Every second, GPS coordinates are recorded along with an accuracy value. I translate the accuracy into a rating scale from 1 to 5 ('weak' to 'spot on'). See the code example below.
Every second, I display the measured position as a magenta circle. Every time the signal strength changes by a full level, I plot a yellow circle and indicate the strength. I connect the dots with a red line. I count how often each accuracy level is found. Which is shown (cryptically short) in the heading, together with the date, for easily comparing screenshots between walks.
In the live app, the circles work best at zoom level 19 or higher. The red line works best at zoom level 18 or lower.
Evaluation: Both iPhones are able to render the route followed with reasonable accuracy when zoomed out. However, upon closer inspection (when zoomed in), the discrepancy can be confusing. The exact position can be off by 10 meters or more from what is reported. During normal use, this can be mitigated by waiting for the blue dot to stabilize, similar to Google Maps. However, in an unstructured area, like a park, it may not be as easy to detect discrepancies using visual cues. We actually need higher precision than Google Maps (since in Google Maps, if the blue dot is a few meters outside a bicycle lane, no one will be confused).